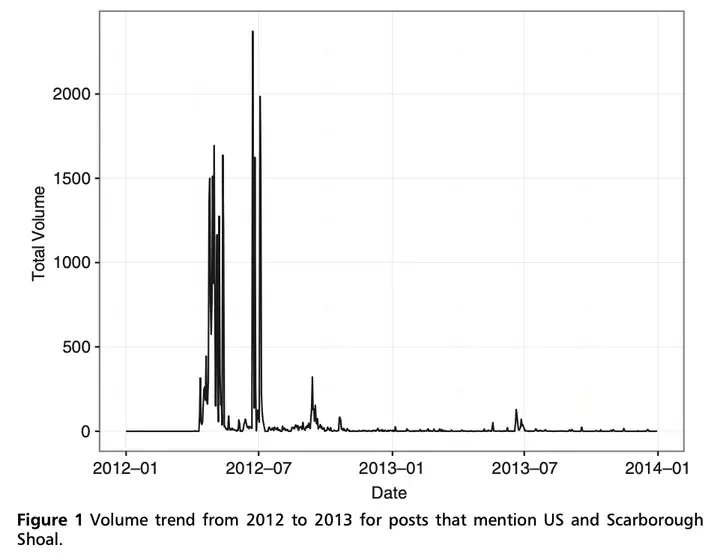
 Number of posts discussing controversial Scarborough Shoal issue and the United States.
Number of posts discussing controversial Scarborough Shoal issue and the United States.Abstract
We study Chinese attitudes toward the United States, and secondarily toward Japan, Russia, and Vietnam, by analyzing social media discourse on the Chinese social media site, Weibo. We focus separately on a general analysis of attitudes and on Chinese responses to specific international events involving the United States. In general, we find that Chinese netizens are much more interested in US politics than US society. Their views of the United States are characterized by deep ambivalence; they have remarkably favorable attitudes toward many aspects of US influence, whether economic, political, intellectual, or cultural. Attitudes toward the United States become negative when the focus turns to US foreign policy – actions that Chinese netizens view as antithetical to Chinese interests. On the contrary, attitudes toward Japan, Russia, and Vietnam vary a great deal from one another. The contrast between these differentiated Chinese views toward the United States and other countries, on the one hand, and the predominant anti-Americanism in the Middle East, on the other, is striking.